Abstract
The Arctic Ocean, though the smallest of the world’s oceans, plays a crucial role in regulating global ecosystems and biogeochemical cycles through its currents and water masses. Nitrogen is the key element responsible for limiting phytoplankton growth and annual primary production in the Arctic Ocean. Climate-induced reductions in sea ice extent and volume are altering the growth conditions for marine phytoplankton, with consequences for the Arctic marine ecosystem.
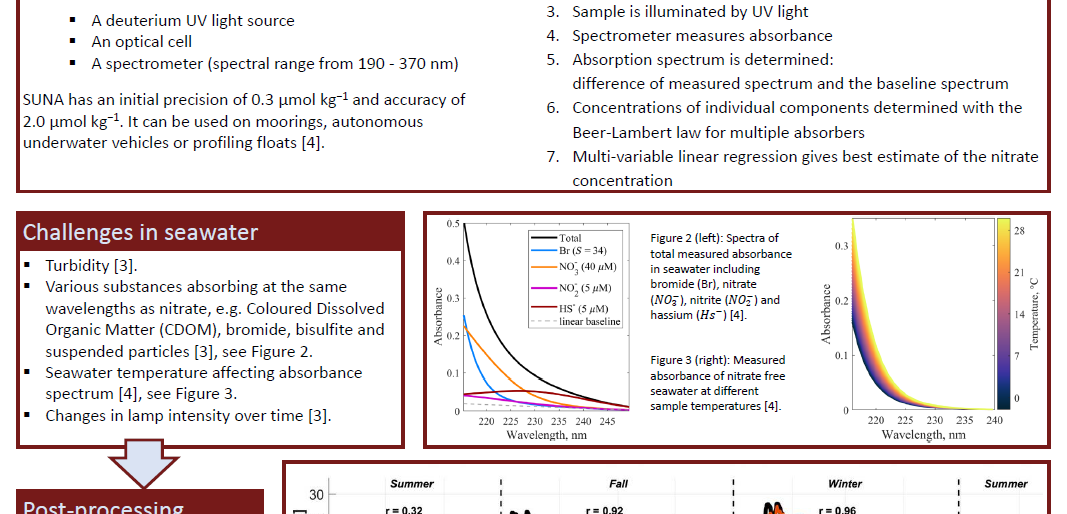
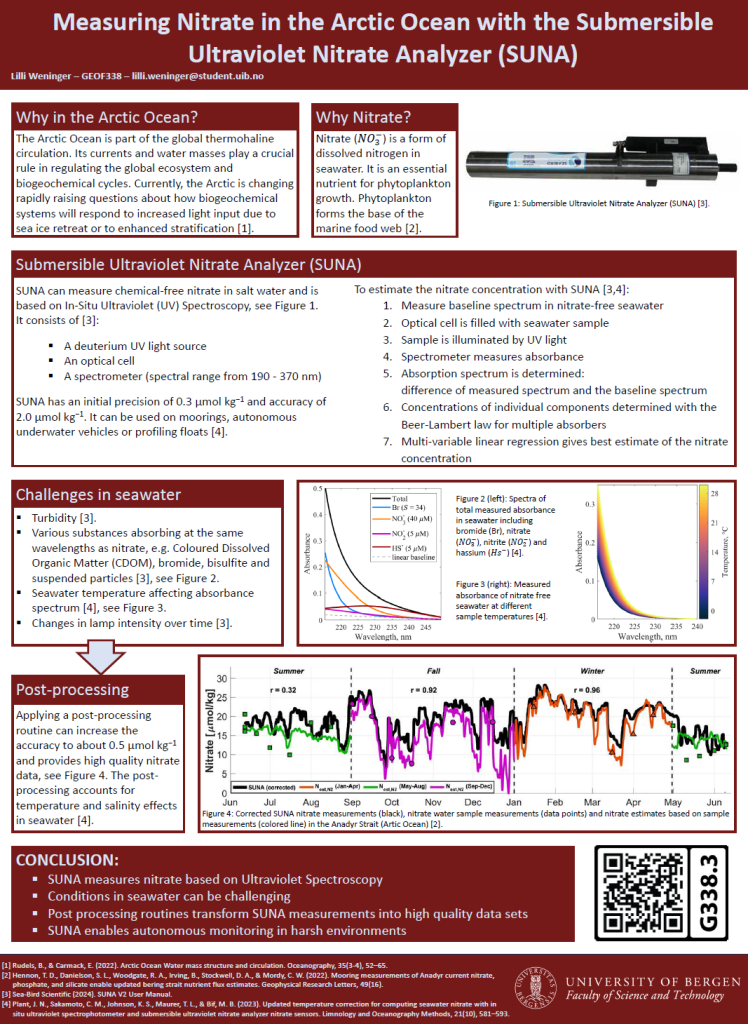
Obtaining high quality data in this region is challenging and autonomous instruments have become essential tools for long-term and continuous monitoring. The Submersible Ultraviolet Nitrate Analyser (SUNA) can measure chemical-free nitrate in fresh, brackish and salt water and is based on In-Situ Ultraviolet Spectroscopy. However, in natural waters, the conditions for SUNA to measure nitrate can be challenging, reducing its accuracy and precision. Nevertheless, with post-processing algorithms and routines it is possible to obtain high quality datasets. SUNA nitrate measurements can thus contribute to the understanding of future changes in the Arctic Ocean and their global implications.